Class
A class defines the properties and behaviors for objects.
A class is a user defined blueprint or prototype from which objects are created. It represents the set of properties or methods that are common to all objects of one type. In general, class declarations can include these components, in order:
- Modifiers : A class can be public or has default access (Refer this for details).
- Class name: The name should begin with a initial letter (capitalized by convention).
- Superclass(if any): The name of the class’s parent (superclass), if any, preceded by the keyword extends. A class can only extend (subclass) one parent.
- Interfaces(if any): A comma-separated list of interfaces implemented by the class, if any, preceded by the keyword implements. A class can implement more than one interface.
- Body: The class body surrounded by braces, { }.
Constructors are used for initializing new objects. Fields are variables that provides the state of the class and its objects, and methods are used to implement the behavior of the class and its objects.
Object
It is a basic unit of Object Oriented Programming and represents the real life entities. A typical Java program creates many objects, which as you know, interact by invoking methods. An object consists of :
- State : It is represented by attributes of an object. It also reflects the properties of an object.
- Behavior : It is represented by methods of an object. It also reflects the response of an object with other objects.
- Identity : It gives a unique name to an object and enables one object to interact with other objects.
Methods in Java
A method is a collection of statements that perform some specific task and return the result to the caller. A method can perform some specific task without returning anything. Methods allow us to reuse the code without retyping the code. In Java, every method must be part of some class which is different from languages like C, C++, and Python.
Methods are time savers and help us to reuse the code without retyping the code.
Methods are time savers and help us to reuse the code without retyping the code.
Method Declaration
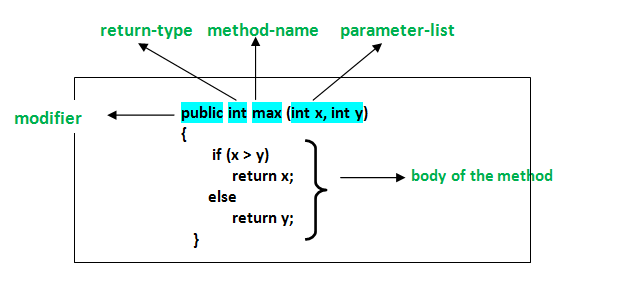
In general, method declarations has six components :
- Modifier-: Defines access type of the method i.e. from where it can be accessed in your application. In Java, there 4 type of the access specifiers.
- public: accessible in all class in your application.
- protected: accessible within the class in which it is defined and in its subclass(es)
- private: accessible only within the class in which it is defined.
- default (declared/defined without using any modifier) : accessible within same class and package within which its class is defined.
- The return type : The data type of the value returned by the method or void if does not return a value.
- Method Name : the rules for field names apply to method names as well, but the convention is a little different.
- Parameter list : Comma separated list of the input parameters are defined, preceded with their data type, within the enclosed parenthesis. If there are no parameters, you must use empty parentheses ().
- Exception list : The exceptions you expect by the method can throw, you can specify these exception(s).
- Method body : it is enclosed between braces. The code you need to be executed to perform your intended operations.
Method signature: It consists of the method name and a parameter list (number of parameters, type of the parameters and order of the parameters). The return type and exceptions are not considered as part of it.
Method Signature of above function:
Method Signature of above function:
max(int x, int y)
How to name a Method?: A method name is typically a single word that should be a verbin lowercase or multi-word, that begins with a verb in lowercase followed by adjective, noun….. After the first word, first letter of each word should be capitalized. For example, findSum,
computeMax, setX and getX
computeMax, setX and getX
What is Class , Object and Method?
![What is Class , Object and Method?]() Reviewed by Pappy
on
September 01, 2019
Rating:
Reviewed by Pappy
on
September 01, 2019
Rating:






No comments: